Namespaces
A Namespace is a communication channel that allows you to split the logic of your application over a single shared connection (also called "multiplexing").
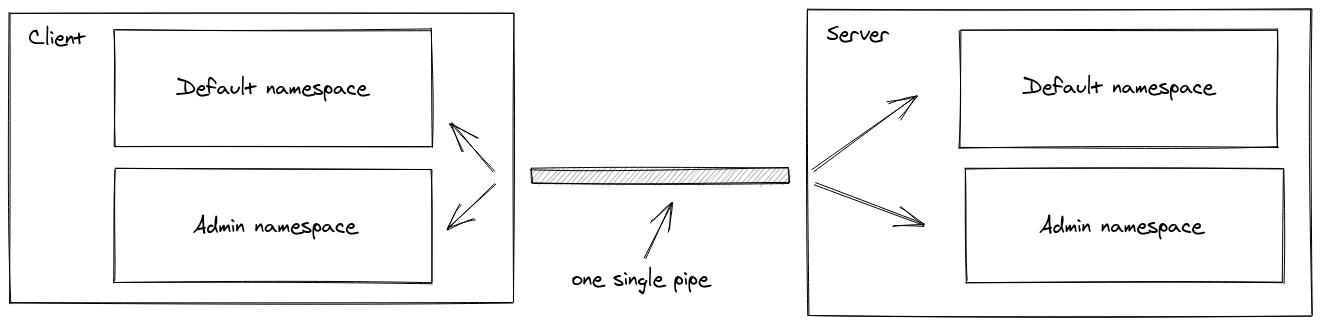
Introduction#
Each namespace has its own:
io.of("/orders").on("connection", (socket) => { socket.on("order:list", () => {}); socket.on("order:create", () => {});});
io.of("/users").on("connection", (socket) => { socket.on("user:list", () => {});});const orderNamespace = io.of("/orders");
orderNamespace.on("connection", (socket) => { socket.join("room1"); orderNamespace.to("room1").emit("hello");});
const userNamespace = io.of("/users");
userNamespace.on("connection", (socket) => { socket.join("room1"); // distinct from the room in the "orders" namespace userNamespace.to("room1").emit("holà");});const orderNamespace = io.of("/orders");
orderNamespace.use((socket, next) => { // ensure the socket has access to the "orders" namespace, and then next();});
const userNamespace = io.of("/users");
userNamespace.use((socket, next) => { // ensure the socket has access to the "users" namespace, and then next();});Possible use cases:
- you want to create a special namespace that only authorized users have access to, so the logic related to those users is separated from the rest of the application
const adminNamespace = io.of("/admin");
adminNamespace.use((socket, next) => { // ensure the user has sufficient rights next();});
adminNamespace.on("connection", socket => { socket.on("delete user", () => { // ... });});- your application has multiple tenants so you want to dynamically create one namespace per tenant
const workspaces = io.of(/^\/\w+$/);
workspaces.on("connection", socket => { const workspace = socket.nsp;
workspace.emit("hello");});Main namespace#
Until now, you interacted with the main namespace, called /. The io instance inherits all of its methods:
io.on("connection", (socket) => {});io.use((socket, next) => { next() });io.emit("hello");// are actually equivalent toio.of("/").on("connection", (socket) => {});io.of("/").use((socket, next) => { next() });io.of("/").emit("hello");Some tutorials may also mention io.sockets, it's simply an alias for io.of("/").
io.sockets === io.of("/")Custom namespaces#
To set up a custom namespace, you can call the of function on the server-side:
const nsp = io.of("/my-namespace");
nsp.on("connection", socket => { console.log("someone connected");});
nsp.emit("hi", "everyone!");Client initialization#
Same-origin version:
const socket = io(); // or io("/"), the main namespaceconst orderSocket = io("/orders"); // the "orders" namespaceconst userSocket = io("/users"); // the "users" namespaceCross-origin/Node.js version:
const socket = io("https://example.com"); // or io("https://example.com/"), the main namespaceconst orderSocket = io("https://example.com/orders"); // the "orders" namespaceconst userSocket = io("https://example.com/users"); // the "users" namespaceIn the example above, only one WebSocket connection will be established, and the packets will automatically be routed to the right namespace.
Please note that multiplexing will be disabled in the following cases:
- multiple creation for the same namespace
const socket1 = io();const socket2 = io(); // no multiplexing, two distinct WebSocket connections- different domains
const socket1 = io("https://first.example.com");const socket2 = io("https://second.example.com"); // no multiplexing, two distinct WebSocket connections- usage of the forceNew option
const socket1 = io();const socket2 = io("/admin", { forceNew: true }); // no multiplexing, two distinct WebSocket connectionsDynamic namespaces#
It is also possible to dynamically create namespaces, either with a regular expression:
io.of(/^\/dynamic-\d+$/);or with a function:
io.of((name, auth, next) => { next(null, true); // or false, when the creation is denied});You can have access to the new namespace in the connection event:
io.of(/^\/dynamic-\d+$/).on("connection", (socket) => { const namespace = socket.nsp;});The return value of the of() method is what we call the parent namespace, from which you can:
- register middlewares
const parentNamespace = io.of(/^\/dynamic-\d+$/);
parentNamespace.use((socket, next) => { next() });The middleware will automatically be registered on each child namespace.
- broadcast events
const parentNamespace = io.of(/^\/dynamic-\d+$/);
parentNamespace.emit("hello"); // will be sent to users in /dynamic-1, /dynamic-2, ...caution
Existing namespaces have priority over dynamic namespaces. For example:
// register "dynamic-101" namespaceio.of("/dynamic-101");
io.of(/^\/dynamic-\d+$/).on("connection", (socket) => { // will not be called for a connection on the "dynamic-101" namespace});Complete API#
The complete API exposed by the Namespace instance can be found here.